Pre-filters capture airborne particulate matter with a particle size of between 3 to 10 microns at an efficiency rate of 70%. They prevent larger particulate matter from clogging up filtration media. Pre-filtration extends the lifespan of the filters by reducing airborne pollutants including dust, dust mites, allergens, and human and pet hair.
Bamboo is a natural material with a complex microstructure, providing excellent particle filtration properties.
Lysozyme is a molecule naturally present in the immune system. It has a very effective action against microbes by attacking their cell walls.
Silver ions are known for their antibacterial and anti-fungal properties.
Eoleaf's multi-layer filtration technology
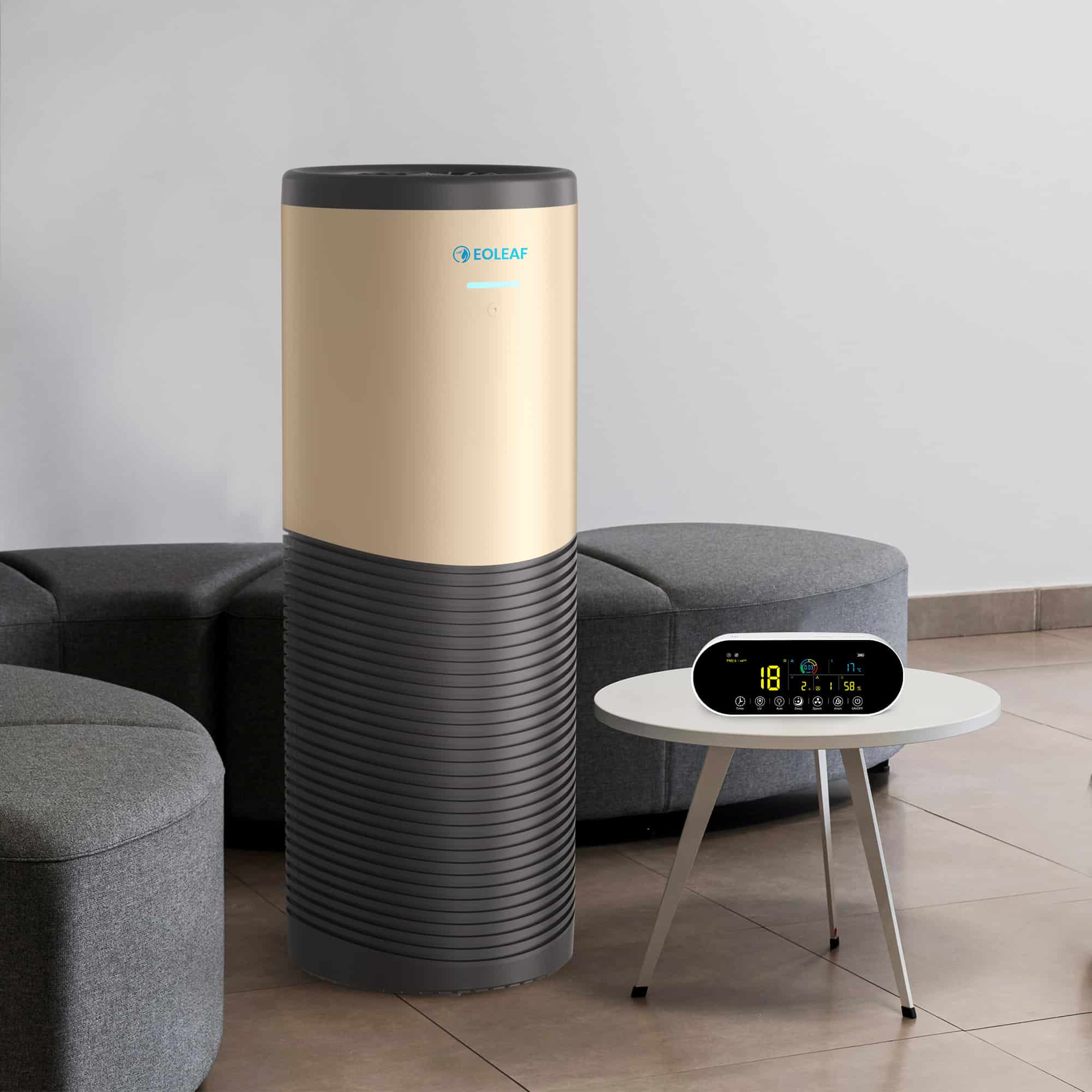
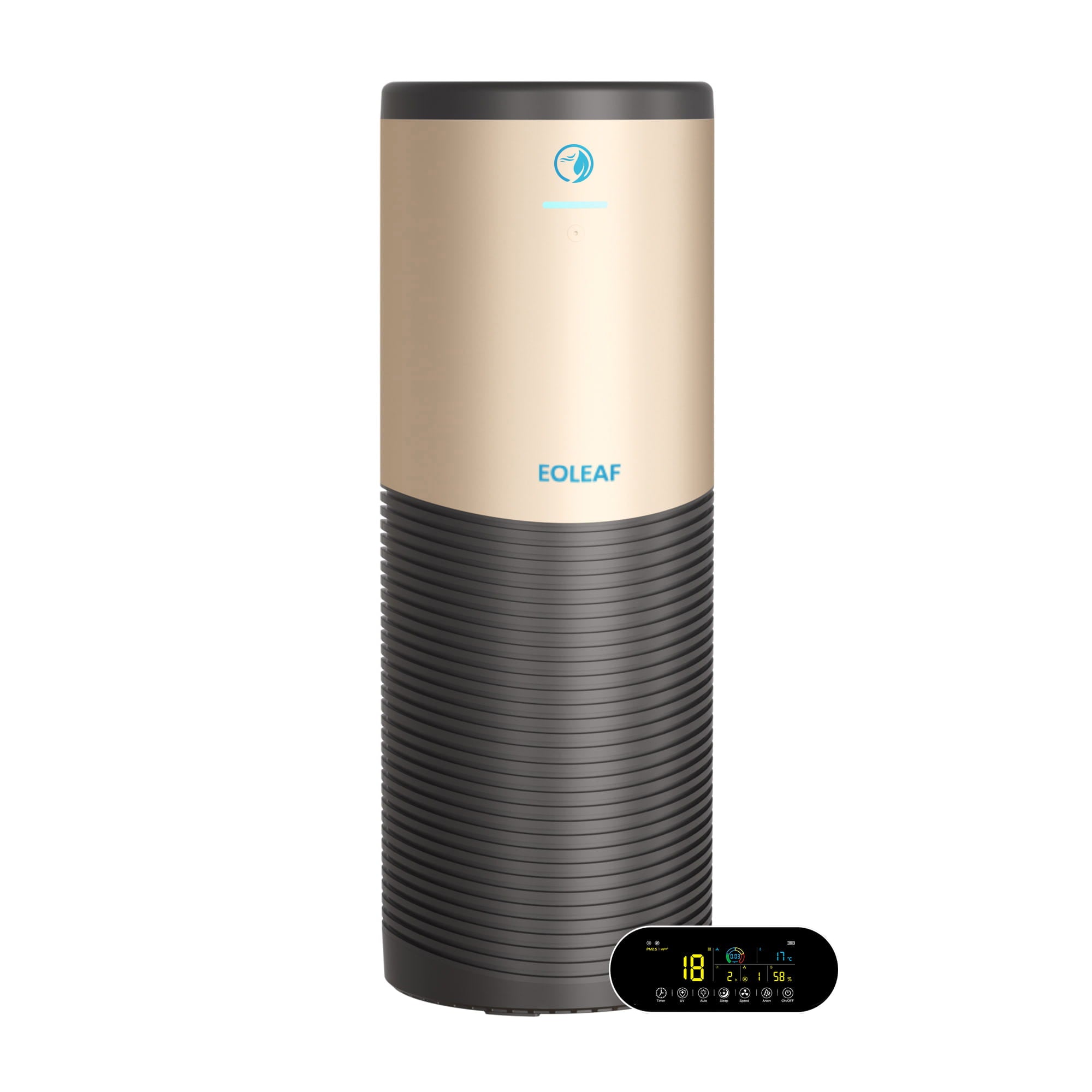
Eoleaf's air purifiers use a combination of best-in-class technologies to filter and purify the air. They rely on a proprietary and innovative 8-step filtration process to remove all pollutants from your indoor air. Our filters contain a multilayer technology: a filter block composed of multiple, successive filters. Not only does that make our technology one of the most advanced and thorough on the market, it also greatly simplifies its maintenance: you only have to change one filter once per year.
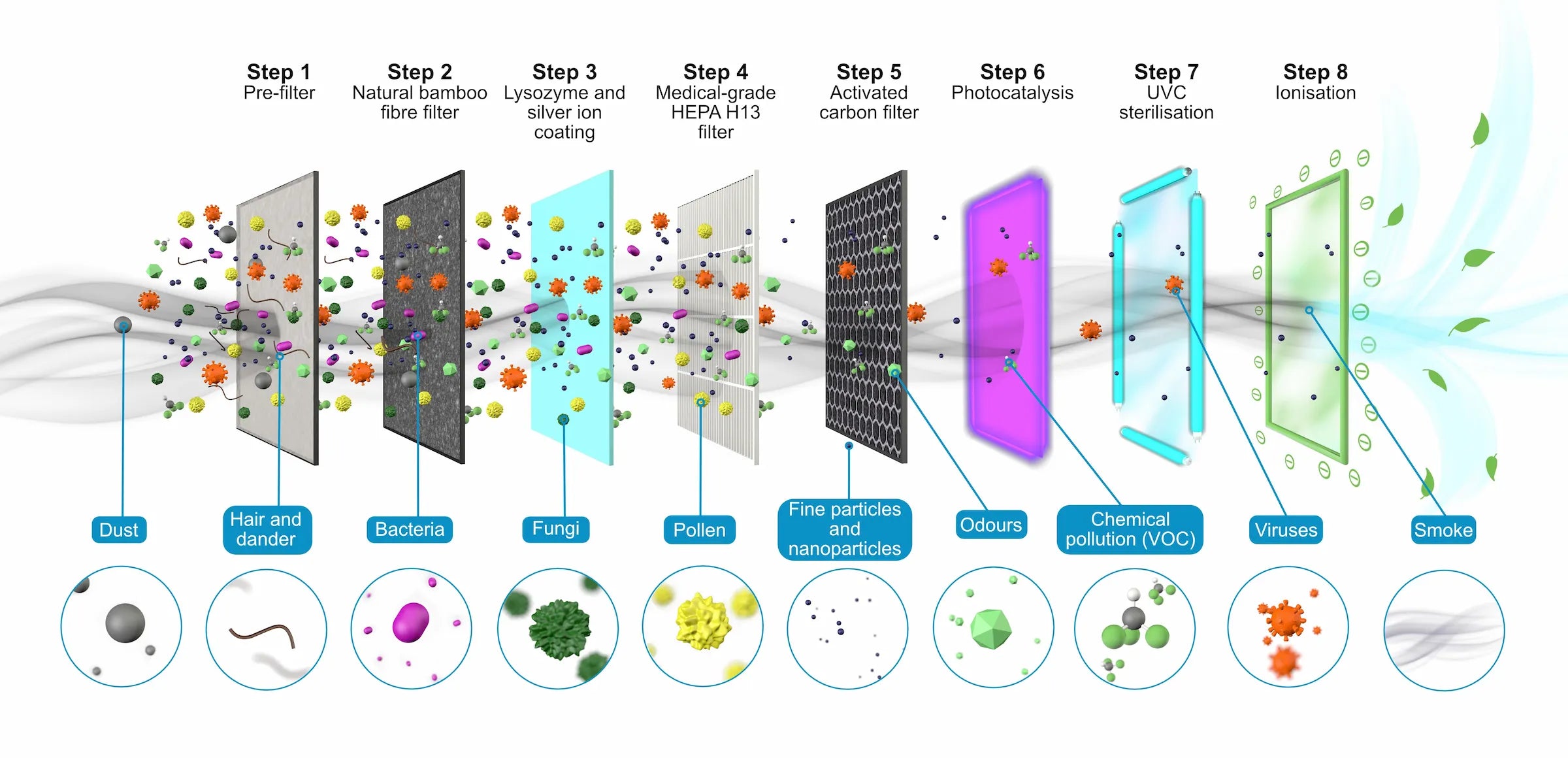
Our 8-step medical-grade filtration process
Most air purifiers on today’s market specialise in one or two air filtration technologies. However, improving your indoor air quality thoroughly is only possible when combining multiple air purification technologies in order to combat all of the different types of indoor air pollution.. Our filtration process consists of a pre-filter, a filter made of natural bamboo fibre with an antibacterial coating composed of silver ions and lysozyme, a medical-grade HEPA H13 filter, an activated carbon filter, photocatalysis, UVC sterilisation, and ionisation (negative ions).

Step 1: Pre-filter
The pre-filter captures all particles larger than one micron (hair, fibres, pet hair, dust).
The purpose of a pre-filter is to help prevent larger air pollutants from clogging up the primary filtration media, thereby extending the life of your air purification filters and device as a whole.
Some examples of airborne pollutants that are caught by pre-filters include dust, allergens, and both human and pet hair.
Step 2: Natural bamboo fibre
Bamboo is a natural material with a complex microstructure, providing excellent particle filtration properties.
Step 3: Lysozyme and silver ion coating
Lysozyme is a molecule naturally present in the immune system. It has a very effective action against microbes by attacking their cell walls.
Silver ions are known for their antibacterial and antifungal properties.
Step 4: Medical-grade HEPA H13 filter
Our HEPA H13 filters are constructed using water-resistant polypropylene fibres. This ensures durability and allows for a 12-month lifespan, one of the longest on the market. This means more high-quality filtration and less frequent filter changes for you, saving you money.
HEPA is a European certification overseen by European standards EN 1822 and EN ISO 29463. A H13 HEPA filter is guaranteed to capture 99.97% of particles with a diameter greater than or equal to 0.01 microns (dust and dust mites, germs like bacteria and viruses, allergens, mould and its spores, fine particles including PM2.5 and PM0.1).
Read more about HEPA filters here.
Step 5: Activated carbon filter
Activated carbon filters (also called activated charcoal) are adsorbent media filters that use granular activated carbon (GAC) or activated charcoal. Charcoal is a carbonaceous material with a porous structure. This structure gives it a high property of fixation and retention of organic, chemical, or gaseous pollution particles (including volatile organic compounds or VOCs)1. It is also particularly effective against unpleasant odours and has the ability to filter both air and water. Activated carbon is also used in cigarette filters, aquariums, and fallout shelters.
In our Eoleaf AEROPRO 40 air purifier, we use 400 g of activated carbon; 640 g in our AEROPRO 100 model; and 1280 g (1.28 kg!) in our AEROPRO 150 model.
Read more about activated carbon here.

Step 6: Photocatalysis
Photocatalytic oxidation, or photocatalysis, is a widely used depollution technology that combines UV (ultraviolet light rays) and a titanium dioxide catalyst to create free electrons. These free electrons are very reactive and quickly bind to VOCs and gases. This then breaks down chemical pollutants into harmless molecules that the filtration within the air purifier can easily capture2,3.
Photocatalysis is very effective against chemical pollution.
Read more about photocatalysis here.
Step 7: Ultraviolet (UVC) sterilisation
UV sterilisation is an extremely effective sterilisation method against all germs. UVC rays, those used in Eoleaf’s products (with a wavelength of 254 nm), are recognized for their effectiveness and harmlessness to humans. This is why they are widely used in the hospital setting: they are both incredibly effective against germs and safe.
Read more about UV sterilisation here.
Step 8: Ionisation (negative ions)
Negative ions are diffused in the ambient air and react with the pollution particles
present in the air (which are positively charged). This then degrades or destroys them. Ionisation is very effective against smoke and fine particles.
Furthermore, there are many studies on the improvement of the feeling of well-being in the presence of negative ions. Researchers have shown that negative ion therapy leads to mental health improvements for those suffering from seasonal and chronic depression5; allergy relief, improved sleep patterns, metabolism moderation, and inhibition of harmful bacteria6; and even improved physical performance for athletes7,8.
Read more about ionisation here.
The benefits of Eoleaf air purifiers:
-
Powerful HEPA-certified filter (up to 670 m3/hr)
-
Discreet and elegant design
-
Easy to use (equipped with Automatic mode) and does not require installation or assembly
-
Can be placed anywhere in your space thanks to our 360° technology
-
Real-time air quality data
Airborne pollutant sizes
Thanks to Eoleaf's high-quality air purifiers, all airborne pollutants are efficiently removed from the air: germs (viruses, bacteria, and mould spores), fine particles and nanoparticles (PM0.1, PM1.0, PM2.5, PM10), allergens (pollen, dust, dust mites, animal dander), chemical pollutants (such as VOCs, formaldehyde, carbon monoxide, and many other toxic gases), smoke (including tobacco smoke, smoke from fires, and exhaust gases), as well as bad odours. All of these pollutants vary enormously in size, hence the importance of combining multiple different filtering technologies. Here are some orders of magnitude:
- Viruses: 0.001 to 0.3 microns
- Particles of the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) virus measure approximately 0.125 microns
- Bacteria: 0.3 to 5 microns
- There are many different varieties of bacteria, meaning that their size varies widely
- Tobacco smoke: 0.3 to 0.5 microns
- Certain particles released by cigarette smoke – typically the most harmful ones – can measure as small as 0.1 microns
- Pet dander: 1 to 5 microns
- Without an air purifier, dander can remain airborne for hours
- Dust and dust mites: 1 to 10 microns
- Mould spores: 5 to 10 microns
- Mould is visible and has a characteristic musty odour
- HEPA air purifier systems work to reduce the number of airborne spores

In summation, Eoleaf air purifiers use a one-of-a-kind, 8-step multilayer technology that guarantees a very broad spectrum of action. Our devices filter all forms of pollution: biological, chemical and particulate.
NeoPur 400 air purifier
40 m² (450 sq ft) coverage area - Smart & Connected
TeraPur 600 air purifier
80 m² (850 sq ft) coverage area - Ultimate all-in-one
AltaPur 700 air purifier
120 m² (1300 sq ft) coverage area - Professional model
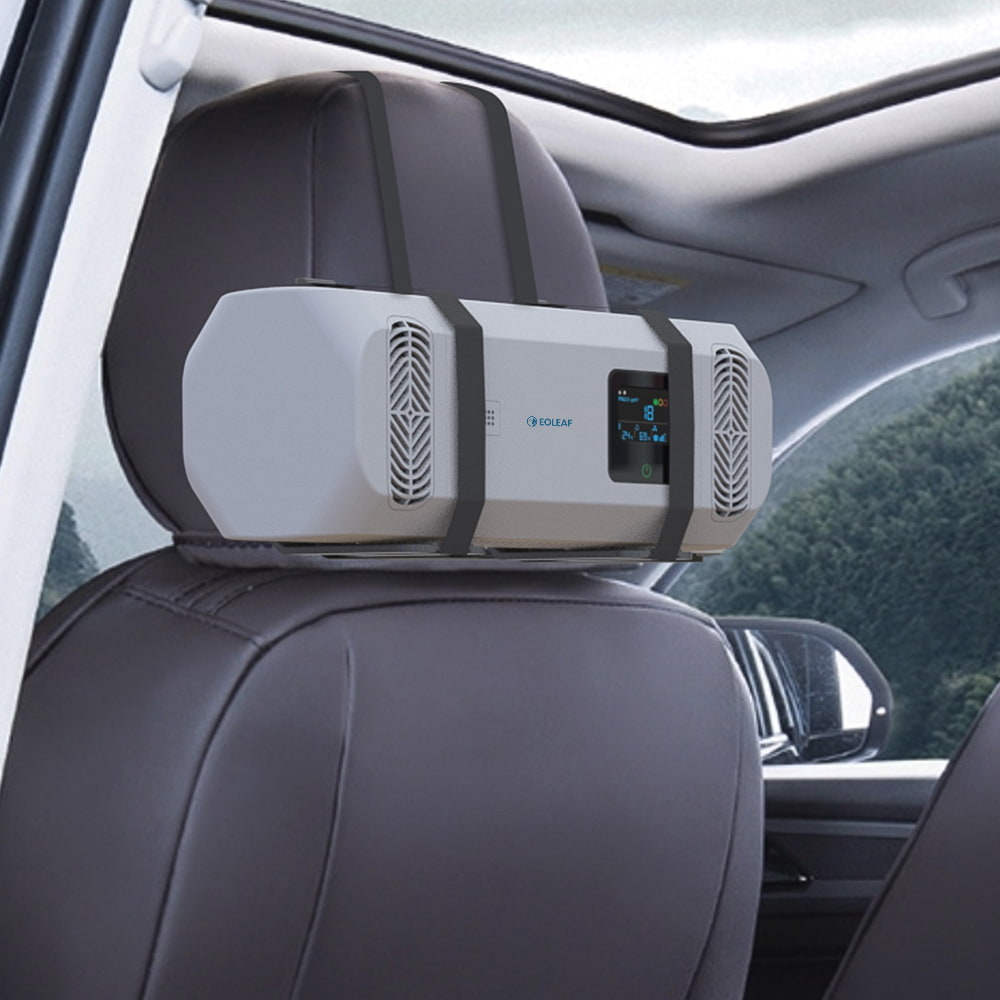
PurCar air purifier
HEPA H13 Filter & Ioniser - For all vehicles
Resources
1 Mondal, S., De, S., & Saha, P. (2019). Removal of vocs and improvement of indoor air quality using activated carbon air filter. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, 123–132. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332110684_Removal_of_VOCs_and_Improvement_of_Indoor_Air_Quality_Using_Activated_Carbon_Air_Filter
2 Zhao, J., & Yang, X. (2003). Photocatalytic oxidation for indoor air purification: A literature review. Building and Environment, 38(5), 645–654. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360132302002123
3 Ren, H., Koshy, P., Chen, W.-F., Qi, S., & Sorrell, C. C. (2017). Photocatalytic materials and technologies for Air Purification. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 325, 340–366. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0304389416307968
4 Dong, W., Liu, S., Chu, M., Zhao, B., Yang, D., Chen, C., Miller, M. R., Loh, M., Xu, J., Chi, R., Yang, X., Guo, X., & Deng, F. (2019). Different cardiorespiratory effects of indoor air pollution intervention with ionization air purifier: Findings from a randomized, double-blind crossover study among school children in Beijing. Environmental Pollution, 254, 113054. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0269749119325060
5 Perez V, Alexander DD, Bailey WH. Air ions and mood outcomes: a review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2013 Jan 15;13:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-13-29. PMID: 23320516; PMCID: PMC3598548.
6 Jiang SY, Ma A, Ramachandran S. Negative Air Ions and Their Effects on Human Health and Air Quality Improvement. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 28;19(10):2966. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102966. PMID: 30274196; PMCID: PMC6213340.
7 Inbar, O., Rotstein, A., Dlin, R. et al. The effects of negative air ions on various physiological functions during work in a hot environment. Int J Biometeorol 26, 153–163 (1982). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02184628
8 Ho CS, Lee MC, Chang CY, Chen WC, Huang WC. Beneficial effects of a negative ion patch on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage, inflammation, and exercise performance in badminton athletes. Chin J Physiol. 2020 Jan-Feb;63(1):35-42. doi: 10.4103/CJP.CJP_33_19. PMID: 32056985.
Eoleaf's range of air purifiers
NeoPur 400 air purifier
40 m² (450 sq ft) coverage area - Smart & Connected
TeraPur 600 air purifier
80 m² (850 sq ft) coverage area - Ultimate all-in-one
AltaPur 700 air purifier
120 m² (1300 sq ft) coverage area - Professional model
PurCar air purifier
HEPA H13 Filter & Ioniser - For all vehicles